Hydroponics and aeroponics
-
2018/10/09
-
THGrow
-
Basic Guide

In this post we are going to see what a hydroponic crop consists of. The word hydroponics comes from the Greek word water + labour. In ancient Rome it was already used to harvest vegetables. When we talk about hydroponic cultivation, we mean that it is not done with organic matter, such as soil, but with other materials with inorganic characteristics, such as vermiculite, rock wool or coconut fibre, among others. These materials act as a support and will be the nutrient solution, rich in minerals, which feeds the plant without the need for natural or organic soil to thrive. The advantage of doing a hydroponic crop is that the crops are optimised throughout the year, as the crops take less time to mature and production increases; there are also savings in water because it is more difficult for it to evaporate and savings in nutrients, as these are not wasted; moreover, less space is needed for the crop. However, we must take into account that it is somewhat more complicated due to the technical issues that must be learned to control, such as pH levels, electroconductivity (EC), nutrient dosage and temperature. In addition, the initial cost is somewhat higher.
Hydroponic system: The first thing we have to use is an aqueous solution or an inert, non-organic substrate. The most common are coconut substrate, vermiculite, rock wool or expanded clay. Therefore, nutrients are added to the water or substrate through irrigation, and it is the grower and not the soil that distributes them.
Some types of substrate:

D) Expanded clay
There are several types of hydroponic cultivation:
Drip cultivation: We need a tank with a water pump connected to a timer to regulate the flow of nutrients at each intake. We will place some plastic trays with sheets of rock wool or similar, and on these we will place the plant rooted in rock wool pots. In this way, we manage to redistribute the water from one plant to the other before returning to the initial deposit. The irrigation will be done through a central pipe with derivations to each pot for a greater efficiency in the transport of nutrients.
Flow and ebb: This system is ideal for small but very leafy plants. We will place the plants in a growing tray full of expanded clay, and under this tray we will have the water tank with the nutrients. In fact, it works like the drainage of a swamp. The water goes up, pushed by the motor pump, floods the growing tray and returns to the tank through some small holes. Some of these hydroponic systems, ideal for beginners and professionals, are the Dutch Pot and the Panda, and if you want something more economical, do not hesitate to get the Aquafarm, very reliable and easy to use.
DWC System (Deep water culture): The plants are placed in special grid pots and held by clay balls (expanded clay). The roots of the plants must be immersed in a tank with the nutrient solution. To prevent the roots from rotting inside the tank we must install a device called a diffuser stone or aquarium oxygenator, which, as its name suggests, serves to oxygenate the water and keep it healthy and free from bacteria that would make our plants sick.
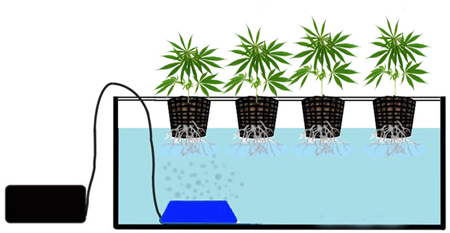 (DWC System)
(DWC System)
You can find at a very reasonable price the DWC Pot that stands out for the simplicity of its handling and because it is a very silent device, suitable for mother plants and plants in flowering phase.
 (DWC Pot)
(DWC Pot)
NFT Nutrient Film Technique: This is a technique that combines several of the above types. The oxygenated watery compound reaches the potting tray. It should be placed at a sufficient angle to allow it to fall back into the tank, to be oxygenated again and to be transferred to the plants. It is a closed circular circuit where the water is in constant movement to guarantee the nutrition of the plants. The system provided by the Grow Tank NFT is very simple to install, achieving faster and more abundant harvests..
 (Grow Tank)
(Grow Tank)
And then we have, finally, the Aeroponia, from the Greek aereo (air) and ponos (work), where there is no type of substrate and it will be small sprinklers that will constantly mist water over the aerial root of the plant. The advantage of aeroponics is a greater oxygenation of the plant's roots, but it is necessary to have a lot of experience in this growing area. Aeroponics is perfect for stimulating growth by achieving large plants, while obtaining larger harvests than when planting in soil or water, but you must be extremely careful so that the plant's roots are adequately oxygenated and vaporized.
We find Aerofarm-type aeroponic systems or the Xstream propagator practical and efficient to use with a design optimised for their purpose.

In summary, the importance of these hydroponic systems lies in the correct oxygenation of the aqueous compound in which the nutrients are dissolved, which in turn will serve as food for the plant from clean water so that we can gradually add the salts that are necessary to control the Electroconductivity (EC). The EC can be measured in several units: we leave you a very useful conversion table to know the equivalences of the different units of measurement.
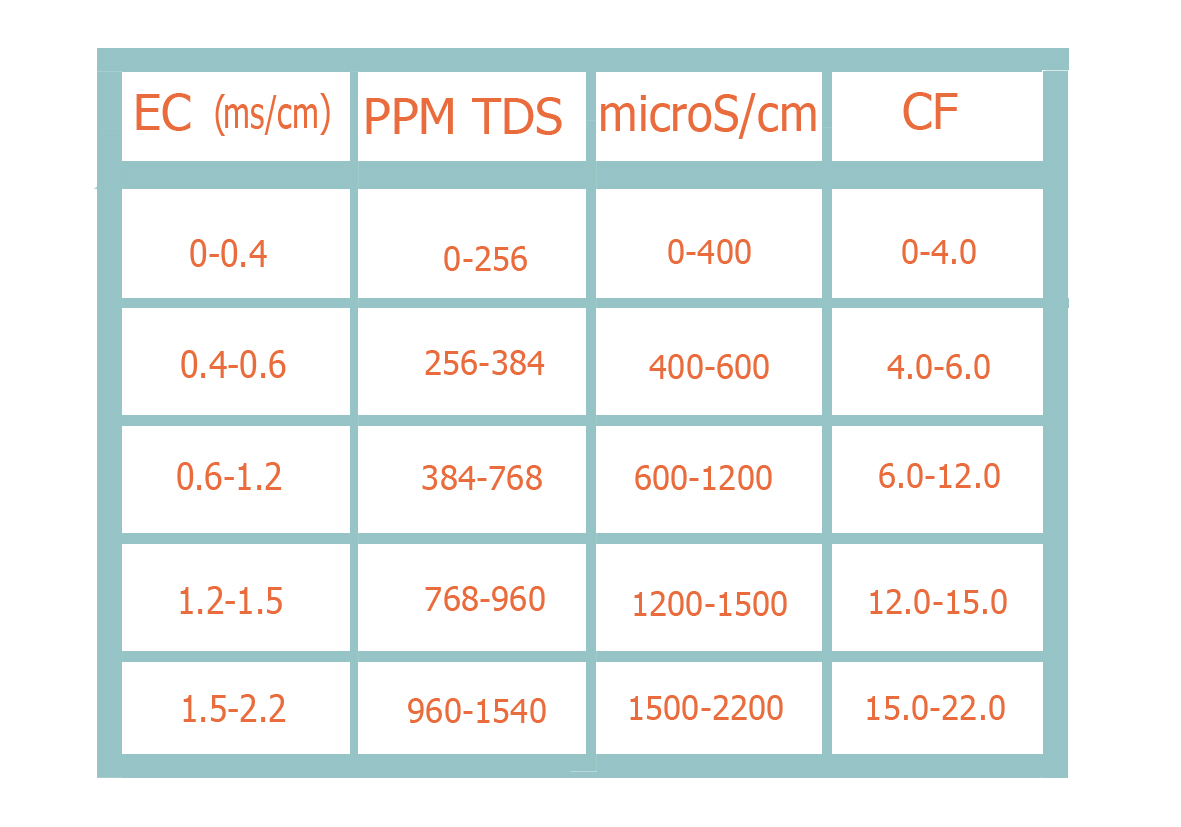
To find out the EC of a solution we must use a meter like the ones you will find on our website.
The ideal way to start preparing the nutrient solution is to start from a low EC and gradually add more fertilizer until the desired EC is reached:
For Cuttings 0.4-0.6
Seedlings: 1.2-1.5
Growth and flowering: 1.5-2.2
We should keep in mind that the fertilizer we use should not be the organic fertilizer we use for soil cultivation, unless the manufacturer expressly recommends it, but as a rule we will use fertilizers indicated for this purpose.
The pH level of the water should be adjusted periodically between 5.5 and 6.5. You can use a pH meter. The pH level of the water should be adjusted periodically between 5.5 and 6.5. You can use a EC eco406 meter and we like it very much:
 (EC eco 406 meter)
(EC eco 406 meter)
Soft water: We call it soft water when its electroconductivity is below 0.4 EC.
Hard water: We call it hard water when its electroconductivity is above 0.4 EC.
During the cultivation of the plant we must vary the electroconductivity of the water, therefore, when the plant has just sprouted the ideal EC is 0.4, but as it grows we must increase the EC to 0.8 EC or 0.9 EC. When the plant is in a process of vigorous growth, we will increase it by 1.2 EC or 1.3 EC and when it reaches flowering, we will increase it to 1.6 EC or 1.8 EC and in some cases, if the plant is very sativa, we could even increase it to 2 EC, but this last point is not frequent.
We must keep in mind that if the water is soft we will have to enrich it with calcium and magnesium salts, on the contrary, if the water is hard we will have to use a reverse osmosis device. On many occasions these devices reduce the EC to really low levels (0.01) and then we must add tap water, previously rested for 24 to 48 hours, and in this way we will reach a more suitable EC (such as 0.4) and then we will add the appropriate fertilizers to the water to obtain the ideal EC.













